Compatibility
There are a small number of requirements for the target software for this fuzzer to support it as a fuzz target. If your project meets the requirements here, it is likely it can use this fuzzer for fuzz testing!
Requirements Overview
TSFFS has two requirements to run:
- Your target software must be running on a CPU model with a supported architecture
- Your target CPU model must support either micro-checkpoints or snapshots
Architecture
Supported Architectures:
- x86_64
- x86
- RISC-V (32 and 64-bit)
If your model’s target architecture is one of these, it is supported by TSFFS. If not, file an issue or pull request. Adding new architectures is easy, and can be a good first contribution to the fuzzer. See the generic and specific architecture information here.
Micro Checkpoints
Micro checkpoints are only supported prior to Simics 7.0.0. If you are using a newer version of Simics, snapshots first.
SIMICS has a feature called micro checkpoints that allows in-memory snapshots of the target software state, as well as reasonably fast restoration of these snapshots to enable fuzzing.
There are different levels of micro checkpoint support – this fuzzer requires only that initialization and code actively under test with the fuzz harness for your project works correctly with micro checkpoints. You can test that micro checkpoints work for your model with a simple test.
Testing Micro Checkpoints
As an example, let’s consider the x86 QSP platform model that ships with SIMICS and the
Hello World EFI resource
example which you can
build by running ./build.sh in the resource directory. The process for fuzzing this
target software follows the basic flow:
- Boot the x86 QSP BIOS with the QSP x86 hdd boot script, with a minimal boot disk
- Upload the test.efi EFI app using the SIMICS agent (for most real targets, we would just boot an image that has our target software EFI app already included).
- Run the test.efi EFI app we uploaded
- While running, the test.efi target software code reaches our start harness, which triggers the beginning of the fuzzing loop by taking a micro checkpoint. The fuzzer continues execution of the target software.
- While running, either a fault is encountered or the software reaches the stop harness. In either case, the fuzzer restores the original micro checkpoint with a new fuzz input, runs the software, and replays this step infinitely.
Set Up The Project
In this case, to test micro checkpoints manually from the SIMICS command line, we can
create a new project (replace 6.0.169 with your installed SIMICS base version):
$ "${SIMICS_HOME}/simics-6.0.169/bin/project-setup" ./test-micro-checkpoints
Project created successfully
$ cd test-micro-checkpoints
This Hello World example project needs the 2096 package, which is for the SIMICS QSP
platform model. Add the package to the project by running (replace 6.0.70 with your
installed SIMICS QSP package version):
$ echo "${SIMICS_HOME}/simics-qsp-x86-6.0.70/" >> ".package-list"
$ ./bin/project-setup
Project updated successfully
We will also add a simics script. Add the contents below as test.simics in the project
root.
$disk0_image = (lookup-file "%simics%/minimal_boot_disk.craff")
run-command-file "%simics%/targets/qsp-x86/qsp-hdd-boot.simics"
script-branch "UEFI Shell Enter Branch" {
local $kbd = $system.mb.sb.kbd
local $con = $system.console.con
local $sercon = $system.serconsole.con
bp.time.wait-for seconds = 10
$kbd.key-press ESC
bp.time.wait-for seconds = 3
foreach $i in (range 2) {
$kbd.key-press KP_DOWN
bp.time.wait-for seconds = .5
}
$kbd.key-press ENTER
bp.time.wait-for seconds = .5
$kbd.key-press KP_UP
bp.time.wait-for seconds = .5
$kbd.key-press ENTER
bp.time.wait-for seconds = .5
$kbd.key-press ENTER
bp.time.wait-for seconds = .5
$con.input "FS0:\n"
bp.time.wait-for seconds = 10
# We are now in the UEFI shell, we'll download our EFI app
local $manager = (start-agent-manager)
$con.input ("SimicsAgent.efi --download " + (lookup-file "%simics%/test.efi") + "\n")
bp.time.wait-for seconds = .5
}
Finally, build and copy the test.efi module and the minimal_boot_disk.craff image
into the project root:
pushd /path/to/this/repo/examples/tests/x86_64-uefi/
ninja
popd
cp /path/to/this/repo/examples/tests/x86_64-uefi/test.efi ./
cp /path/to/this/repo/examples/rsrc/minimal_boot_disk.craff ./
Test Micro Checkpoints
To test micro checkpoints, run SIMICS in the project with the script you just created:
$ ./simics test.simics
Intel Simics 6 (build 6218 linux64) © 2024 Intel Corporation
Use of this software is subject to appropriate license.
Type 'copyright' for details on copyright and 'help' for on-line documentation.
[board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0] info] VMP disabled. Failed to open device.
WARNING: Simics failed to enable VMP. Enabling VMP substantially improves
simulation performance. The problem is most likely caused by the
vmxmon kernel module not being properly installed or updated.
See the "Simics User's Guide", the "Performance" section,
for instructions how to setup VMP.
NAPT enabled with gateway 10.10.0.1/24 on link ethernet_switch0.link.
NAPT enabled with gateway fe80::2220:20ff:fe20:2000/64 on link ethernet_switch0.link.
simics>
SIMICS is now running, and we can continue through the boot process all the way into
the EFI shell on filesystem FS0 by running run:
simics> run
[board.mb.sb.lpc.bank.cs_conf unimpl] Write to unimplemented field cs_conf.oic.aen (0x31ff) (value written = 0x01, contents = 0x00), will not warn again.
[board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0] unimpl] Writing to unimplemented MSR 0x1f2 (ia32_smrr_physbase), value = 0xdf800006
[board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0] unimpl] Writing to unimplemented MSR 0x1f3 (ia32_smrr_physmask), value = 0xff800000
[board.mb.sb.lpc.bank.acpi_io_regs unimpl] Write to unimplemented field acpi_io_regs.smi_en.EOS (0x30) (value written = 0x00000001, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0] unimpl] Reading from unimplemented MSR 0x1f3 (ia32_smrr_physmask), value = 0xff800000
[board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0] unimpl] Writing to unimplemented MSR 0x1f3 (ia32_smrr_physmask), value = 0xff800800
[board.mb.sb.spi.bank.spi_regs spec-viol] Write to read-only field spi_regs.hsfsts.fdv (value written = 0x0000, contents = 0x0001).
[board.mb.sb.thermal.bank.pci_config spec-viol] Enabling bus master, but this device doesn't support it
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Read from unimplemented register csr.extcnf_ctrl (0x00000f00) (contents = 0x00000000).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented register csr.extcnf_ctrl (0xf00) (value written = 0x00000020).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.tctl.rrthresh (0x400) (value written = 0x00000000, contents = 0x00000001), will not warn again.
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Read from unimplemented register csr.fwsm_s (0x00005b54) (contents = 0x00000000).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented register csr.strap (0xc) (value written = 0x00008086).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] Read from poorly or non-documented register csr.dummy_3004 (contents = 0).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] Write to poorly or non-documented register csr.dummy_3004 (value written = 0x50000, contents = 0).
[board.mb.sb.phy.bank.mii_regs unimpl] Write to unimplemented register mii_regs.vendor_specific[15] (0x3e) (value written = 0x6094).
[board.mb.sb.phy.bank.mii_regs unimpl] Read from unimplemented register mii_regs.vendor_specific[4] (0x0028) (contents = 0x0000).
[board.mb.sb.phy.bank.mii_regs unimpl] Write to unimplemented register mii_regs.vendor_specific[4] (0x28) (value written = 0x0000).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] writing 0 to count is not allowed
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] writing 0 to count is not allowed
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Read from unimplemented register csr.eec (0x00000010) (contents = 0x00000000).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Read from unimplemented register csr.ledctl (0x00000e00) (contents = 0x00000000).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.tx_queue[0].txdctl.pthresh (0x3828) (value written = 0x0000001f, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.tx_queue[0].txdctl.wthresh (0x3828) (value written = 0x00000001, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.tx_queue[0].txdctl.gran (0x3828) (value written = 0x00000001, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.tx_queue[1].txdctl.pthresh (0x3928) (value written = 0x0000001f, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.tx_queue[1].txdctl.wthresh (0x3928) (value written = 0x00000001, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.tx_queue[1].txdctl.gran (0x3928) (value written = 0x00000001, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] Read from poorly or non-documented register csr.dummy_5b00 (contents = 0).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] Write to poorly or non-documented register csr.dummy_5b00 (value written = 0xffffffc0, contents = 0).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] Read from poorly or non-documented register csr.sec (contents = 0).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] writing 0 to count is not allowed
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr spec-viol] writing 0 to count is not allowed
[board.mb.sb.lan spec-viol] access to reserved register at offset 0x280c in CSR bank
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented register csr.h2me (0x5b50) (value written = 0x00000000).
[board.mb.sb.phy.bank.mii_regs unimpl] Read from unimplemented register mii_regs.vendor_specific[3] (0x0026) (contents = 0x0000).
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.ctrl.rfce (0) (value written = 0x00000001, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[board.mb.sb.lan.bank.csr unimpl] Write to unimplemented field csr.ctrl.tfce (0) (value written = 0x00000001, contents = 0x00000000), will not warn again.
[matic0 info] The Simics agent has terminated.
[matic0 info] disconnected from UEFI0 (0x1b90f02e10d5a84c)
running>
You’ll see several automatic actions on the SIMICS GUI, and you will end up with the console screen below.
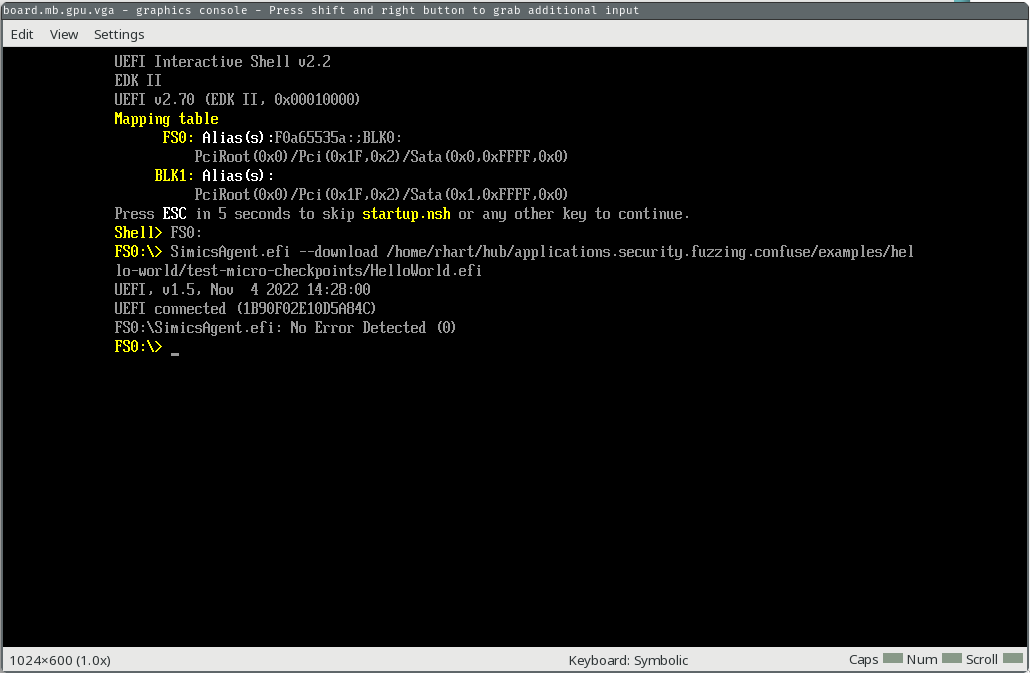
First, we’ll run our EFI app to make sure all is well.
running> $system.console.con.input "test.efi\n"
You should see “Working…” print out on the console.
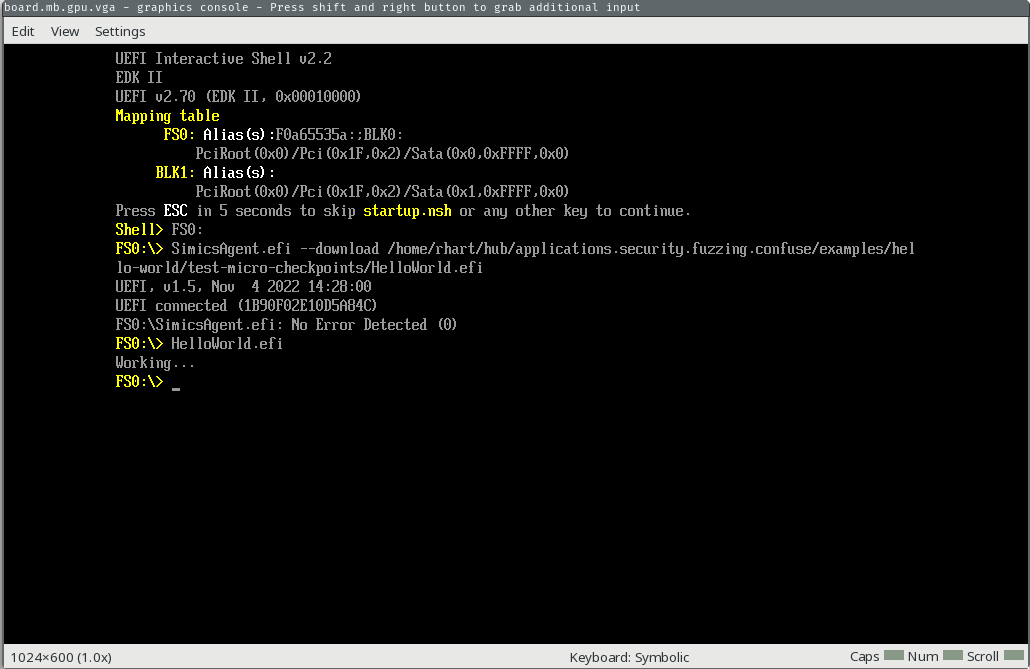
Now, we’ll go ahead stop the simulation and take our micro checkpoint.
running> stop
simics> @VT_save_micro_checkpoint("origin", 0)
None
Our simulation is now stopped, with a checkpoint just taken. We’ll run the EFI app again and continue, then stop the simulation after the app finishes running.
simics> $system.console.con.input "test.efi\n"
simics> continue
running> stop
We stopped our execution after the app executed, so you should see the output from the second time we ran it (“Working…”) printed on the GUI console.
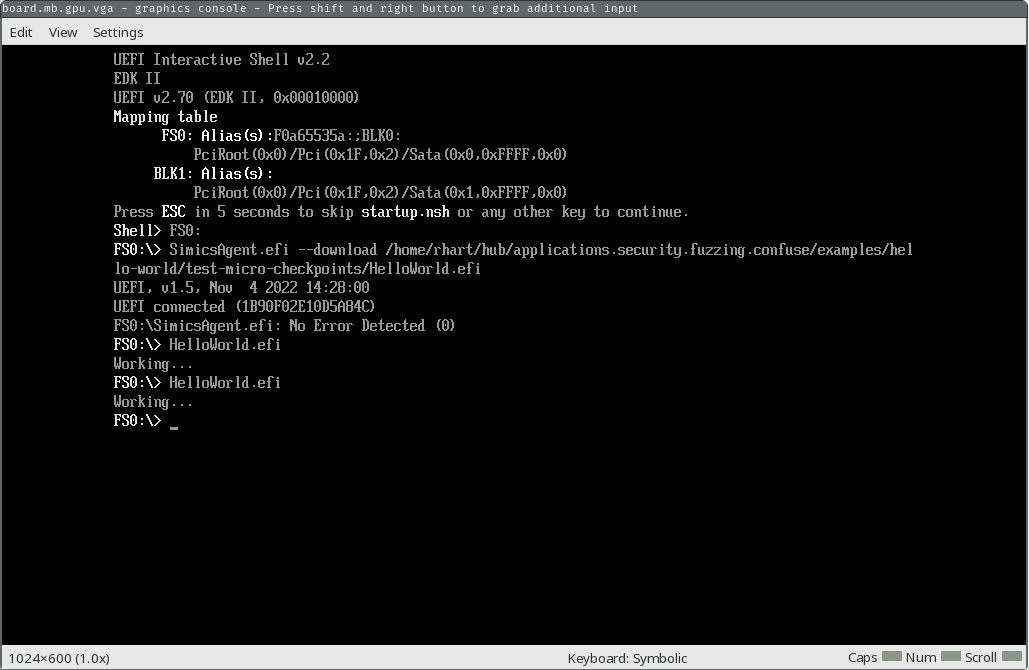
Now, we will restore our micro checkpoint and clear the recorder. The second step is important, because if we did not clear the recorder we would replay the execution of the app.
simics> @VT_restore_micro_checkpoint(0)
None
simics> @CORE_discard_future()
None
simics> continue
The console should be back to the state it was before you ran the second app execution, and will look like this:

Testing for Your App
What you want to fuzz will depend on your project, so this procedure will change somewhat depending on your project. In general, try to follow this flow:
- Save a micro checkpoint
- Run whatever software you want to fuzz in a normal configuration, for example via a test case you already have
- Restore the micro checkpoint
- Make sure everything is reset as you expect it to be, for example if your software relies on register values or filesystem objects, make sure they are reset.
- If you are able, do this several times. Some issues can occur on many executions that are not apparent after just one, for example if your model has a memory leak. You can script this step if you’d like.
Snapshots
Newer versions of SIMICS (>= 7.0.0) support a new feature called snapshots, which are similar to micro checkpoints but do not rely on underlying rev-exec support. If your model supports a new version of SIMICS, follow the same instructions as for micro checkpoints, but replace:
VT_save_micro_checkpoint("origin", 0)withVT_save_snapshot("origin")VT_restore_micro_checkpoint(0)withVT_restore_snapshot("origin")
And do not call CORE_discard_future.