Queues and Queue Pairs
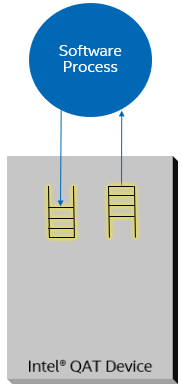
Communication between CPU and Intel® QuickAssist Technology hardware is via hardware-assisted queues (aka rings):
Queues are circular buffers.
Memory is in System DRAM.
Device is configured with base address, entry size and number of entries via device CSRs.
Head and Tail pointers are in device CSRs (MMIO space).
Queues Pairs
To send a request, software writes request descriptor to next available entry in the request queue, and updates the tail pointer.
Device firmware reads request descriptor from request queue, updating the head pointer. It then processes the request, writes response descriptor onto response queue, and updates the tail pointer.
Response queues can be configured to generate an interrupt when device firmware updates the tail pointer, or can be polled.
Queue Bundles
Queues are grouped into bundles of 8 queues (4 Queue Pairs (QPs)).
When SR-IOV is enabled, each bundle shows up as a separate Virtual Function.
Within each bundle, by default, a separate QP is used for each of the three possible services:
Public Key Crypto
Symmetric Crypto
Data Compression
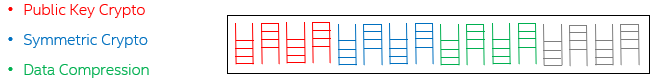
Max of 2 service types per QAT device at a time. Each QP can be allocated to a specific service, in a bare metal environment.