Load Balancing
Per Endpoint
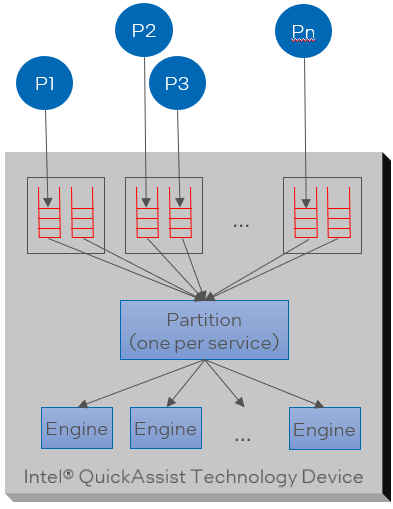
There are four arbiters, which by default are used for the different services (with one spare/unused).
Each partition:
Arbitrates across two request queues per bundle/VF, to pick a request.
Load balances all of these requests across all available “engines”.
Within a partition, arbitration uses round robin.
Ensures fairness (in terms of number of requests) across queue pairs and guests
Across Endpoints
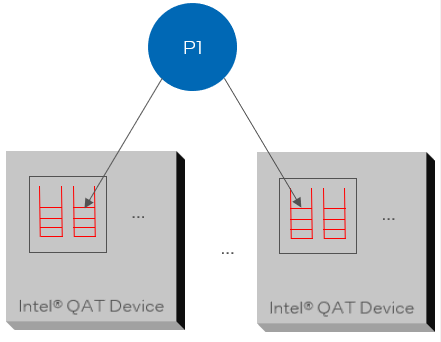
In a platform or CPU with multiple Intel® QAT devices, software is responsible for load sharing across devices/endpoints. Sapphire Rapids has up to four Intel® QAT devices/endpoints in a single CPU package (depending on SKU) PCIe card may have multiple (QAT 1.x) devices across one or more chipsets.
Software-based Load Sharing can be implemented at various layers:
For applications using the Intel® QuickAssist Technology API, the application must implement load balancing.
For applications using a framework (e.g. OpenSSL), the framework implements load balancing.
Load Sharing Criteria
Simple round-robin scheme recommended.
May want to consider “locality” in a multi-socket (NUMA) platform.
Dimensions
Gen 1 |
Gen 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Intel® Communication Chipset 8925 to 8955 Series |
Intel® C62x Chipset |
Intel Atom® Processor C3000 |
|
Number PCIe Endpoints |
1 |
3 |
1 |
Number of Bundles /VFs per Endpoint |
32 |
16 |
16 |
Number of Queue Pairs per Bundle |
8 |
||
Gen 3 |
Gen 4 |
|
|---|---|---|
Intel® Atom P5000 Processor/ Ice Lake D |
Intel® 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processor (per socket) |
|
Number PCIe Endpoints |
1 |
4 |
Number of VFs per Endpoint |
128 |
16 |
Number of Queue Pairs per Bundle |
8 |
4 |