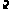 conf.board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0], callback, None)
simics> c
packet received in snooper
packet received in snooper
[...]
conf.board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0], callback, None)
simics> c
packet received in snooper
packet received in snooper
[...]
Ethernet links provide a special interface to listen to all traffic on the link via a function callback. This makes it possible to write simple traffic dumping scripts with customized output.
typedef void (*ethernet_link_snoop_t)(lang_void *user_data,
conf_object_t *clock,
const frags_t *packet,
eth_frame_crc_status_t crc_status);
SIM_INTERFACE(ethernet_snoop) {
conf_object_t *(*attach)(conf_object_t *NOTNULL link,
conf_object_t *clock,
ethernet_link_snoop_t snoop_fun,
lang_void *user_data);
};
#define ETHERNET_SNOOP_INTERFACE "ethernet_snoop"
This interface is implemented by Ethernet link objects. It is used to attach snoop functions to the link. The snoop function will receive all traffic going over the link.
This interface should only be used for inspection, and never as part of the actual simulation. The snoop functions must not affect the simulation in any way.
The clock parameter tells the link on which clock to post the events that call the snoop function. The snoop function will be called at the delivery time of the network packet, which means that it will be called at the same time as any Ethernet devices attached to the same clock that receives packets from the same link.
Snooped frames with a matching CRC will contain the correct frame check sequence.
The user_data parameter is passed to the snoop function every time it is called.
We will use the QSP-x86 as an example. Please start
the simulation with the firststeps-no-network.simics start
script, a simple script callback could be written as follow:
simics> load-module eth-links
simics> new-ethernet-switch link0
Created instantiated 'ethernet_switch' component 'link0'
simics> connect link0.device0 board.mb.sb.eth_slot
# a callback that does nothing but print a warning
simics> @def callback(user_data, clock, packet, crc_status):
simics> print("packet received in snooper")
........
# callback registration on link0, using the CPU as clock object
simics> @ep = conf.link0.link.iface.ethernet_snoop.attach(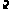 conf.board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0], callback, None)
simics> c
packet received in snooper
packet received in snooper
[...]
conf.board.mb.cpu0.core[0][0], callback, None)
simics> c
packet received in snooper
packet received in snooper
[...]
The endpoint object returned by the attach() function can be destroyed as any time using SIM_delete_object(), ending the capture. Snooper endpoints are used by the external monitoring tools system described in the previous section to feed to the tools the packets passing on the links.