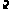 MAC:10:10:10:10:10:01
MAC:10:10:10:10:10:01
A service node can act as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) server, responding to requests from clients that can read their network configuration from such a server. The DHCP protocol is an extension of the BOOTP protocol, and for many uses the feature set is more or less the same. The Simics implementation uses the same configuration for both services.
The service node has a table that maps MAC addresses to IP addresses and domain name. This is used to answer DHCP or BOOTP requests.The <service_node_comp>.add-host command can add entries to this table:
simics> sn0.add-host 10.10.0.1 node1 mac="10:10:10:10:10:01" Adding host info for IP 10.10.0.1: node1.network.simMAC:10:10:10:10:10:01
The <service_node_comp>.list-host-info command prints the current contents of the table:
simics> sn0.list-host-info IP name.domain MAC ------------------------------------------------- 10.10.0.0 simics0.network.sim 20:20:20:20:20:00 10.10.0.1 node1.network.sim 10:10:10:10:10:01
The <service_node_comp>.dhcp-add-pool command adds dynamic DHCP leases, from which new clients will be automatically assigned an address on request. When an entry from the pool is given out, the new mapping is stored in the internal host info table, including a generated name that can be found through DNS queries. If a DHCP client's MAC address matches an entry in the table, it is assigned the corresponding IP address. If there is no matching MAC address, the dynamic address pools will be searched for an available IP address.
The DHCP implementation in service-node is simple, and might not work with all DHCP clients.