Intel® Enterprise AI Foundation for OpenShift*
Overview
The project delivers a comprehensive full-stack solution for the Intel® Enterprise AI Foundation on the OpenShift platform, applicable across data center, cloud, and edge environments. It utilizes innovative General Operators technology to provision AI accelerators, including the Intel Gaudi Processor, Flex and Max GPUs, and Xeon CPU accelerators such as QAT, SGX, and DSA. Additionally, the project introduces solutions for integrating Gaudi Software or OneAPI-based AI software into OpenShift AI. Key AI workload integrations, such as LLM inferencing, fine-tuning, and post-training for enterprise AI, are under development. The plans also include the GPU network provisioning and full-stack integration with OpenShift.
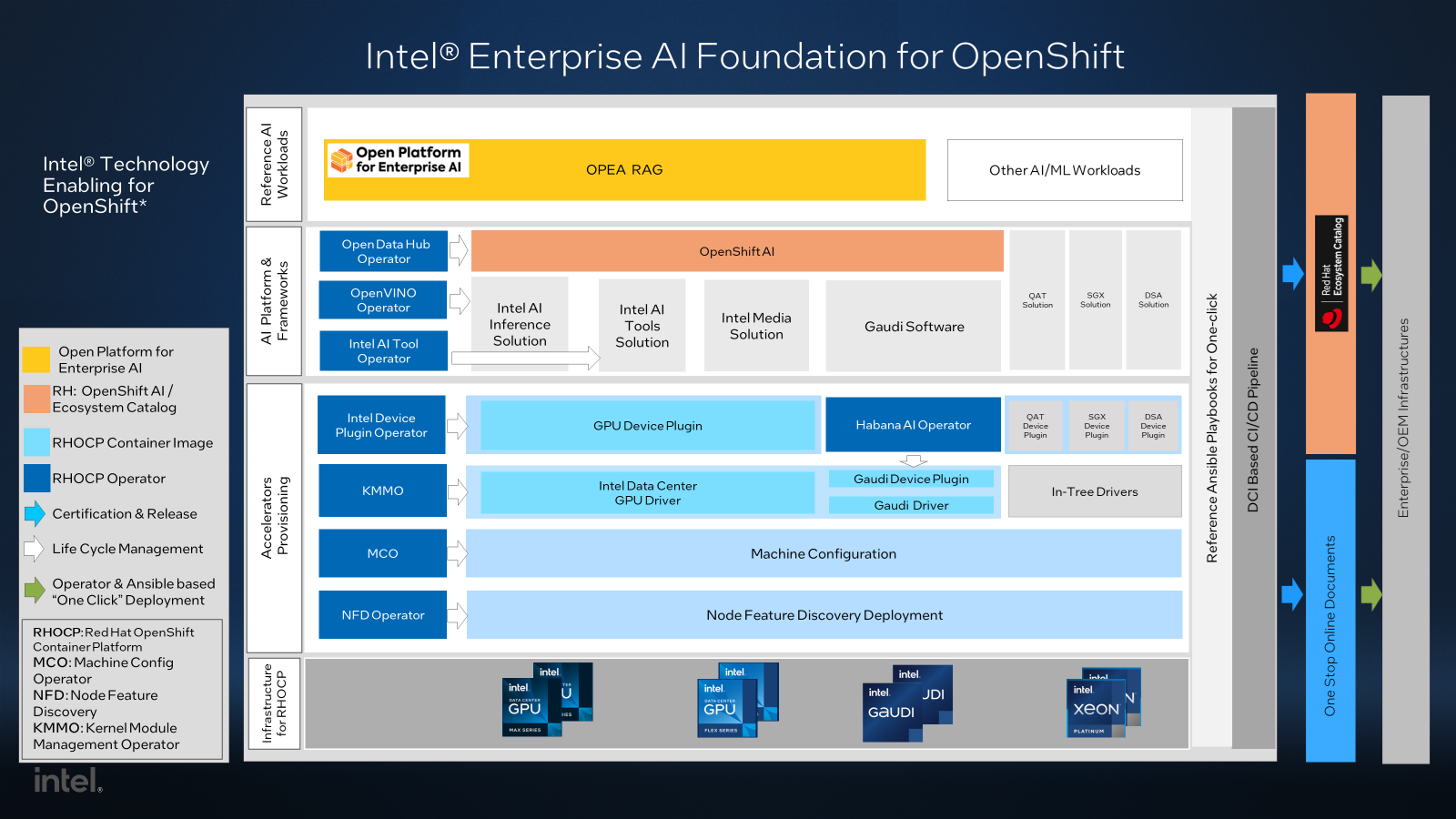
Infrastructure Foundation for Enterprise AI workloads
This project delivers reference infrastructures powered by Intel AI hardware and software technologies, tailored for the cutting-edge enterprise GenAI workloads and seamlessly integrated with the Red Hat AI platform.
The recommended Infrastructure Cluster is built with Intel® scalable Gaudi® Accelerator and standard servers. The Intel® Xeon® processors are used in these Gaudi servers as worker nodes and in standard servers as highly available control plane nodes. This infrastructure is designed for high availability, scalability, and efficiency in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and other Large Language Model (LLM) inferencing workloads.
The Gaudi embedded RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) network, along with the 3 Ply Gaudi RoCE Network topology supports high-throughput and low latency LLM Parallel Pre-training and Post-training workloads, such as Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). For more details, see: Training and fine-tuning LLM Models with Intel Enterprise AI Foundation on OpenShift
This highly efficient infrastructure has been validated with cutting-edge enterprise AI workloads on the production-ready OpenShift platform, enabling users to easily evaluate and integrate it into their own AI environments.
Additionally, Intel SGX, DSA, and QAT accelerators (available with Xeon processors) are supported to further enhance performance and security for AI workloads.
For more details, see: Supported Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (RHOCP) Infrastructure
AI Accelerators & Network Provisioning
Provisioning AI accelerators and networks on a scalable OpenShift/Kubernetes cluster while ensuring the manageability of AI infrastructure and platforms presents significant challenges. To address this, the general Operator concept has been proposed and implemented in this project.
OpenShift/Kubernetes Operators automate the management of the software stack, streamlining AI infrastructure provisioning. Rather than relying on a single monolithic operator to handle the entire stack, the operator best practice - “do one thing and do it well” - is applied. This industrial-leading approach significantly simplifies both Operator development and the AI provisioning process.
Intel® Network Operator allows automatic configuring and easier use of RDMA NICs with Intel AI accelerators.
Intel® Device Plugins Operator handles the deployment and lifecycle of the device plugins to advertise Intel AI accelerators and other Hardware feature resources to OpenShift/Kubernetes.
Kernel module management (KMM) operator manages the deployment and lifecycle of out-of-tree kernel modules like Intel® Data Center GPU Driver for OpenShift*
Machine config operator (MCO) provides an unified interface for the other general operators to configure the Operating System running on the OpenShift nodes.
Node Feature Discovery (NFD) Operator detects and labels AI hardware features and system configurations. These labels are then used by other general operators.
Intel® Converged AI Operator will be used in the future to simplify the usage of the general operators to provision Intel AI features as a stable and single-entry point.
The Other general Operators can be added in the future to extend the AI features.
Red Hat AI Platform with Intel AI technologies
Intel and Red Hat have coordinated for years to deliver a production-quality open-source AI platform, built on the best provision of the Intel AI Accelerator computing and networking technologies.
The Red Hat AI portfolio, powered by Intel AI technologies, now includes:
Red Hat AI Inference Server leverages the LLM-d and vLLM projects, integrating with Llama Stack, Model Context Protocol (MCP), and the Open AI API to deliver standardized APIs for developing and deploying OPEA-based and other production-grade GenAI applications scalable across edge, enterprise and cloud environments.
Red Hat OpenShift AI Distributed Training provides pre-training, SFT and RL for major GenAI foundation models at scale. With seamless integration of the Kubeflow Training Operator, Intel Gaudi Computing and RoCE Networking technology, enterprises can unlock the full potential of cutting-edge GenAI technologies to drive innovation in their domains. See Training and fine-tuning LLM Models with Intel Enterprise AI Foundation on OpenShift.
The operators to integrate Intel Gaudi Software or OneAPI-based AI software into OpenShift AI
Releases and Supported Platforms
Intel Enterprise AI foundation for OpenShift is released in alignment with the OpenShift release cadence. It is recommended to use the latest release.
For details on supported features and components, refer to the links below:
To review the release history, please visit the following link:
Getting started
See reference BIOS Configuration required for each feature.
Provisioning RHOCP cluster
Use one of these two options to provision an RHOCP cluster:
Use the methods introduced in RHOCP documentation.
Use Distributed CI as we do in this project.
In this project, we provisioned RHOCP 4.18 on a bare-metal multi-node cluster. For details about the supported RHOCP infrastructure, see the Supported Platforms page.
Provisioning Intel hardware features on RHOCP
If you are familiar with the steps mentioned below to provision the accelerators, you can use One-Click solution as a reference to provision the accelerator automatically.
Follow Setting up HabanaAI Operator to provision Intel Gaudi AI accelerator.
Please follow the steps below to provision the hardware features
Setting up Node Feature Discovery
Setting up Machine Configuration
Setting up Out of Tree Drivers
Setting up Device Plugins
Verifying hardware feature provisioning
You can use the instructions in the link to verify the hardware features provisioning.
Upgrade (To be added)
Reference end-to-end solution
The reference end-to-end solution is based on Intel hardware feature provisioning provided by this project.
Intel AI Inferencing Solution with OpenVINO and RHOAI
Reference workloads
Here are the reference workloads built on the end-to-end solution and Intel hardware feature provisioning in this project.
Advanced Guide
This section discusses architecture and other technical details that go beyond getting started.
Release Notes
Check the link for the Release Notes.
Support
If users encounter any issues or have questions regarding Intel Technology Enabling for OpenShift, we recommend them to seek support through the following channels:
Commercial support from Red Hat
This project relies on features developed and released with the latest RHOCP release. Commercial RHOCP release support is outlined in the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform Life Cycle Policy and Intel collaborates with Red Hat to address specific requirements from our users.
Open-Source Community Support
Intel Technology Enabling for OpenShift is run as an open-source project on GitHub. Project GitHub issues can be used as the primary support interface for users to submit feature requests and report issues to the community when using Intel technology provided by this project. Please provide detailed information about your issue and steps to reproduce it, if possible.
Contribute
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
Security
To report a potential security vulnerability, please refer to security.md file.
License
Distributed under the open source license. See LICENSE for more information.
Code of Conduct
Intel has adopted the Contributor Covenant as the Code of Conduct for all of its open source projects. See CODE_OF_CONDUCT file.